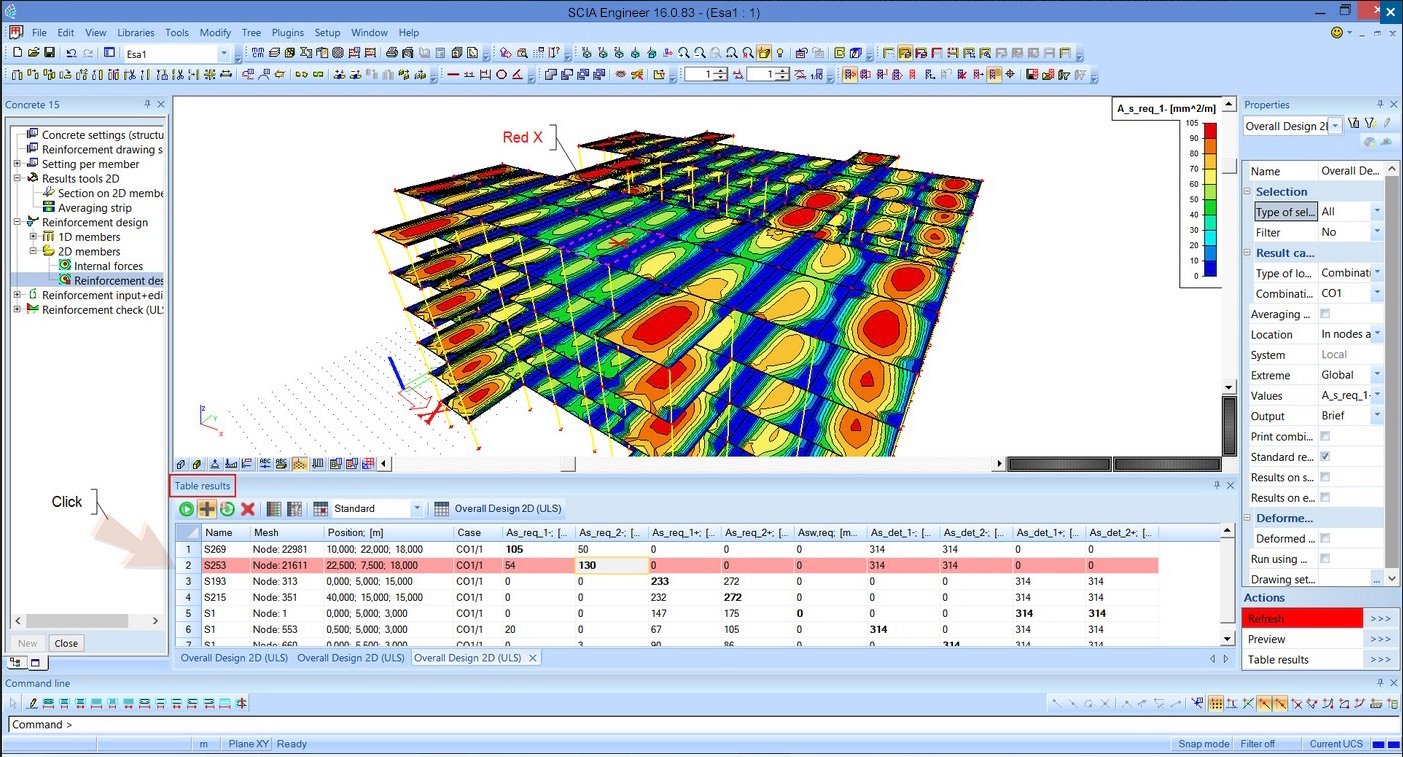
This involves understanding how different parts or subsystems interact with one another
to create the overall structure and function of an organization. A structural approach offers
several advantages over other perspectives in terms of providing insights into complex
systems, facilitating problem solving, and promoting collective action.Moreover,
it can be used in both quantitative and qualitative research contexts. Analysis is a process by which an observer evaluates qualitative or quantitative
observations in order to form a judgment about their worth or meaning. It is a critical
tool for understanding events and phenomena and for making decisions about how to respond
to or manage them. The main aim of analysis is to understand the meaning and significance of
something. The process of analysis can be divided into two main categories: descriptive and
inferential. Descriptive analysis is the first stage of analysis and involves gathering as much information
as possible about the observation. This information can be gathered through observation,
interviews, or questionnaire responses. It helps to give a comprehensive understanding of
the observation under examination. Descriptive analysts aim to provide a comprehensive
description of the observed phenomenon. Inferential analysis is the second stage of analysis and involves drawing conclusions about
the observation. This is done by using established principles or models to make assumptions
about the observed phenomena. Inferential analysts use the information gathered in the
previous stages to form conclusions about the observed phenomenon. The Structural View of Analysis is a model of analysis that provides a structural view of the
phenomenon under examination. The Structural View of Analysis helps to organize and
summarize the information gathered in the descriptive and inferential stages of analysis.
The Structural View of Analysis is useful for making informed decisions about the observed
phenomenon. The Structural View of Analysis is based on the assumption that all observations have structure.
All phenomena have a structure that can be observed and analyzed.
The structure of an observation can be observed through the use of categories, dimensions,
and types. The structure of an observation can also be observed through the use of variables
and relationships. The Structural View of Analysis helps to organize and summarize the
information gathered in the descriptive and inferential stages of analysis.
The Structural View of Analysis is useful for making informed decisions about the observed
phenomenon.